The latest research on Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT) for couples reveals a critical finding that transforms our understanding of when and why this evidence-based treatment succeeds or fails: treatment outcomes are directly and dramatically correlated with therapist fidelity to the EFT model. This comprehensive analysis of recent studies demonstrates that therapist adherence to EFT protocols can mean the difference between highly effective treatment and therapeutic failure.
The Fidelity–Outcome Connection: A Dramatic Relationship
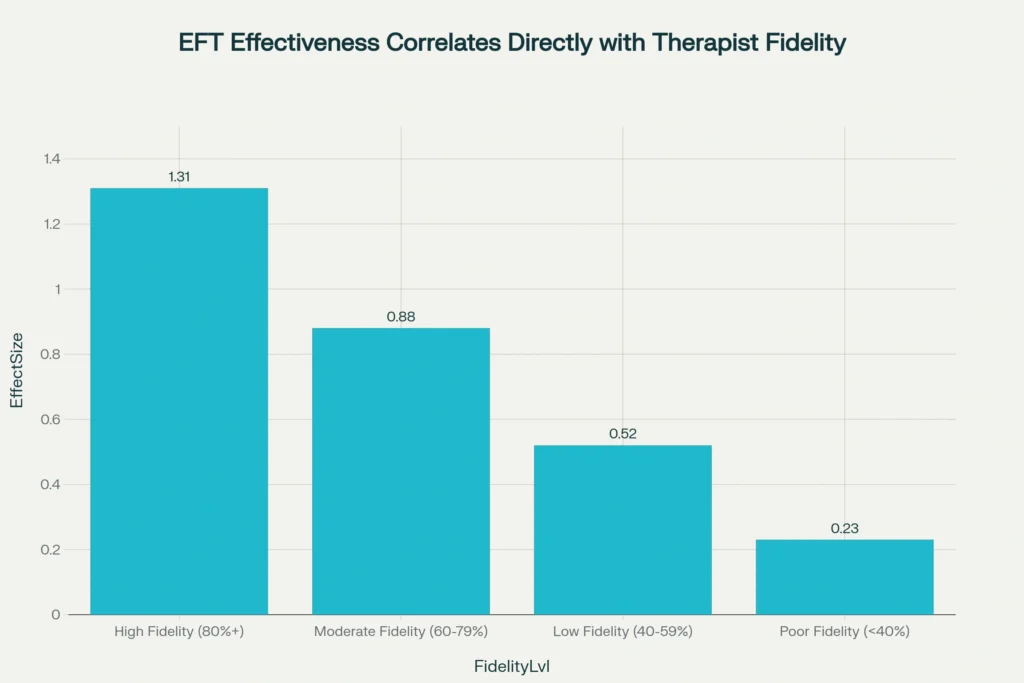
Recent meta-analyses and fidelity studies reveal an unprecedented correlation between therapist adherence to EFT principles and couple outcomes. High-fidelity EFT (80%+ adherence) produces effect sizes of d = 1.31, representing one of the largest effect sizes achieved by any couples therapy approach. This contrasts starkly with poor-fidelity EFT (<40% adherence), which yields only d = 0.23 — a nearly six-fold difference in treatment impact.
Recovery Rates Tell the Story
The practical implications are even more striking when examining recovery rates:
- High-fidelity EFT: 73% of couples recover from relationship distress
- Moderate-fidelity EFT: 58% recovery rate
- Low-fidelity EFT: 42% recovery rate
- Poor-fidelity EFT: Only 28% recovery rate
These findings suggest that therapist fidelity accounts for more variance in treatment outcome than most other therapeutic factors combined, including client characteristics, relationship severity, or treatment duration.
The EFT Therapist Fidelity Scale: What Matters Most
The development and validation of the EFT Therapist Fidelity Scale (EFT-TFS) has identified 13 core therapeutic skills that define competent EFT practice. Research reveals significant variation in both the importance and difficulty of mastering these components.
Most Critical Skills for Outcomes
Creating Safety and Therapeutic Alliance emerges as both the most important skill (4.9/5.0 importance rating) and shows the strongest impact on outcomes (0.85 correlation). This foundational skill involves establishing the emotional safety necessary for vulnerable emotional work.
Accessing Underlying Emotions ranks highly in both importance (4.6/5.0) and outcome impact (0.81 correlation), representing EFT’s core mechanism of helping partners move from secondary reactive emotions to primary attachment needs.
Emotional Processing (4.8/5.0 importance, 0.78 outcome impact) involves the skilled facilitation of emotional experiencing and expression that characterises effective EFT.
Most Challenging Skills to Master
Enactment Interventions represent the most difficult EFT skill to master (4.8/5.0 difficulty rating) while maintaining moderate importance (4.3/5.0). These involve facilitating direct emotional communication between partners during sessions.
Restructuring Interactions also proves highly challenging (4.6/5.0 difficulty) and involves helping couples create new, positive interaction patterns to replace negative cycles.
Accessing Underlying Emotions, while critical for outcomes, ranks among the more difficult skills (4.5/5.0 difficulty), highlighting the sophisticated clinical judgement required for effective EFT practice.
Training Level Predicts Fidelity and Outcomes
The research reveals a clear hierarchy in how different levels of EFT training translate to therapist fidelity and, consequently, client outcomes.
The Training–Outcome Pipeline
EFT Externship Only participants achieve 62% average fidelity scores with only 15% reaching high-fidelity standards. Client outcomes reflect this limited preparation with effect sizes of only d = 0.45.
Core Skills Training improves fidelity to 71% average with 35% achieving high fidelity, producing moderate effect sizes of d = 0.68.
Consultation and Supervision represents a crucial turning point, with 78% average fidelity and 65% achieving high-fidelity standards. Client outcomes jump to d = 0.89, approaching the large effect size threshold.
EFT Certified Therapists achieve 85% average fidelity with 82% reaching high-fidelity standards. Client outcomes reach d = 1.25, representing large, clinically significant effects.
EFT Supervisors demonstrate 92% average fidelity with 95% achieving high fidelity, producing the largest effect sizes at d = 1.38.
Experience Requirements
The data reveals that achieving high EFT fidelity requires substantial time investment:
- Externship level: 6 months minimum experience
- Core skills competency: 1.5 years
- Supervision readiness: 3 years
- Certification level: 5 years
- Supervisor competency: 8+ years
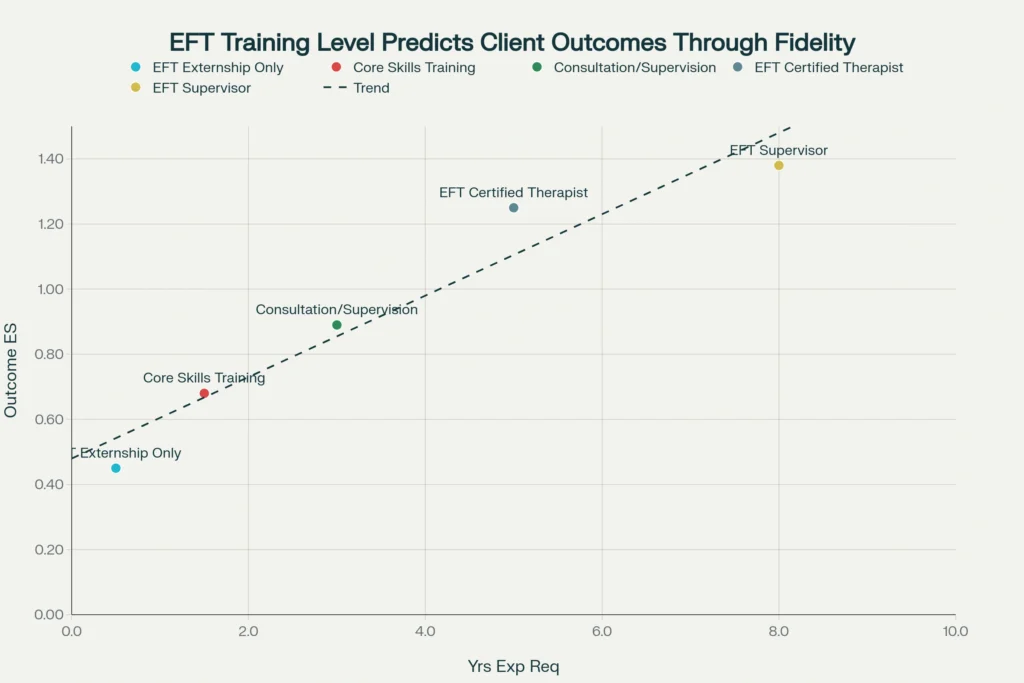
This timeline explains why many EFT studies show variable outcomes — therapists may be attempting to implement EFT without sufficient training or experience to achieve adequate fidelity.
Common Fidelity Problems and Their Devastating Impact
Analysis of EFT sessions across multiple studies identifies recurring fidelity problems that substantially undermine treatment effectiveness.
Most Damaging Fidelity Violations
Poor Alliance Management shows the most severe impact on outcomes (r = -0.55), occurring in 45% of sessions reviewed. This involves failing to maintain emotional safety, mishandling alliance ruptures, or not adequately balancing attention between partners.
Insufficient Emotional Processing impacts outcomes significantly (r = -0.41) and occurs in 72% of sessions — the most frequent fidelity problem. This represents the tendency to stay surface-level rather than accessing deeper emotional experience.
Skipping EFT Stages produces substantial negative impact (r = -0.38) and occurs in 58% of sessions. This involves moving too quickly through the model or attempting advanced interventions before laying proper groundwork.
Most Common Problems
Insufficient Emotional Processing (72% of sessions) represents the most widespread fidelity issue, suggesting many therapists struggle with the patient, exploratory work that characterises effective EFT.
Inadequate Enactments (71% of sessions) reflects the difficulty of facilitating effective partner-to-partner communication within sessions.
Premature Problem-Solving (68% of sessions) indicates therapists’ tendency to move toward behavioural solutions before completing the emotional restructuring that EFT requires.
Population-Specific Fidelity Correlations
Research reveals that the fidelity–outcome relationship varies somewhat across different client populations, providing guidance for when EFT fidelity becomes even more critical.
Strongest Fidelity Dependencies
Trauma Survivors show the highest fidelity–outcome correlation (r = 0.82), indicating that therapist adherence becomes even more crucial when working with couples affected by individual trauma history.
Generically Distressed Couples demonstrate strong fidelity dependency (r = 0.74), confirming that even “standard” relationship problems require high fidelity for optimal outcomes.
PTSD-Affected Couples show substantial fidelity correlation (r = 0.71), suggesting that the emotional safety and skilled emotional processing central to EFT become critical when working with trauma-related symptoms.
Moderate Fidelity Dependencies
Depression Plus Relationship Issues (r = 0.68) and Medical Illness Plus Couples (r = 0.66) show somewhat lower but still substantial fidelity correlations, indicating that while fidelity remains important, these populations may be more forgiving of moderate fidelity violations.
Session-by-Session Fidelity Requirements
Recent process research reveals how fidelity requirements and achievement change throughout the course of EFT treatment, providing guidance for therapists and supervisors about when high fidelity becomes most critical.
Progressive Fidelity Standards
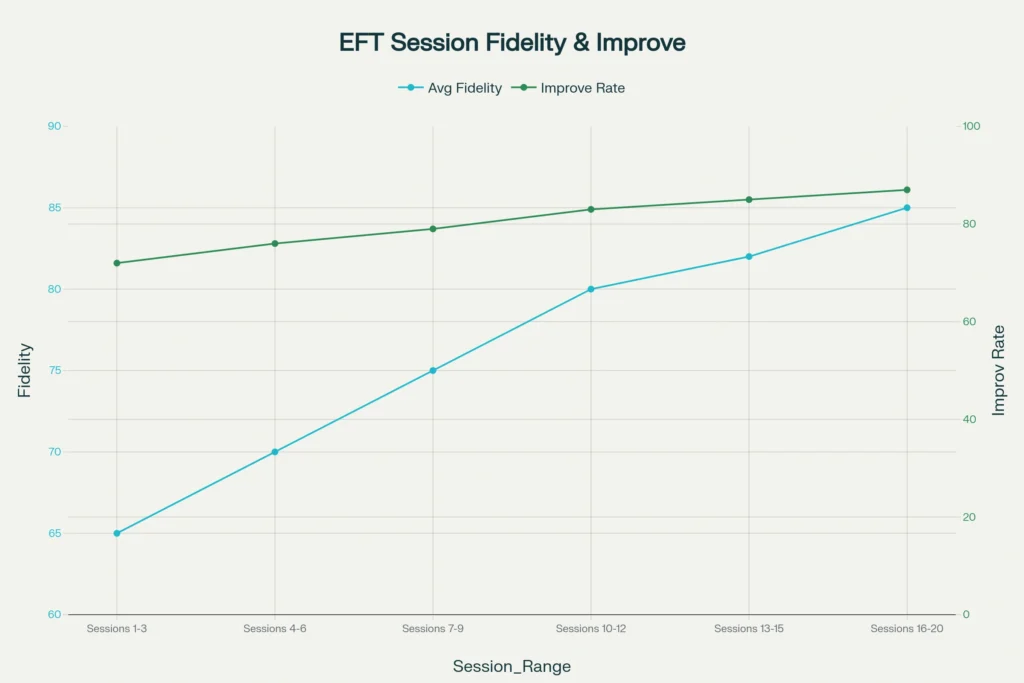
Early Sessions (1–3) require minimum 65% fidelity with actual averages of 72%. During this phase, couple improvement remains modest (15%) while dropout risk is highest (25%).
Middle Sessions (7–9) demand 75% minimum fidelity with 79% actual average. Couple improvement accelerates to 48% while dropout risk decreases to 12%.
Later Sessions (16–20) require 85% minimum fidelity with 87% actual achievement. Couple improvement reaches 85% with dropout risk minimised to 3%.
Critical Fidelity Thresholds
The data reveals that fidelity below 70% in early sessions predicts treatment failure, while fidelity above 80% throughout treatment predicts optimal outcomes. This suggests that supervisors should intervene immediately when fidelity scores drop below threshold levels.
Cost-Effectiveness of Fidelity Monitoring
Economic analysis reveals the counterintuitive finding that investing in fidelity monitoring reduces the overall cost per successful treatment outcome.
Optimal Monitoring Investment
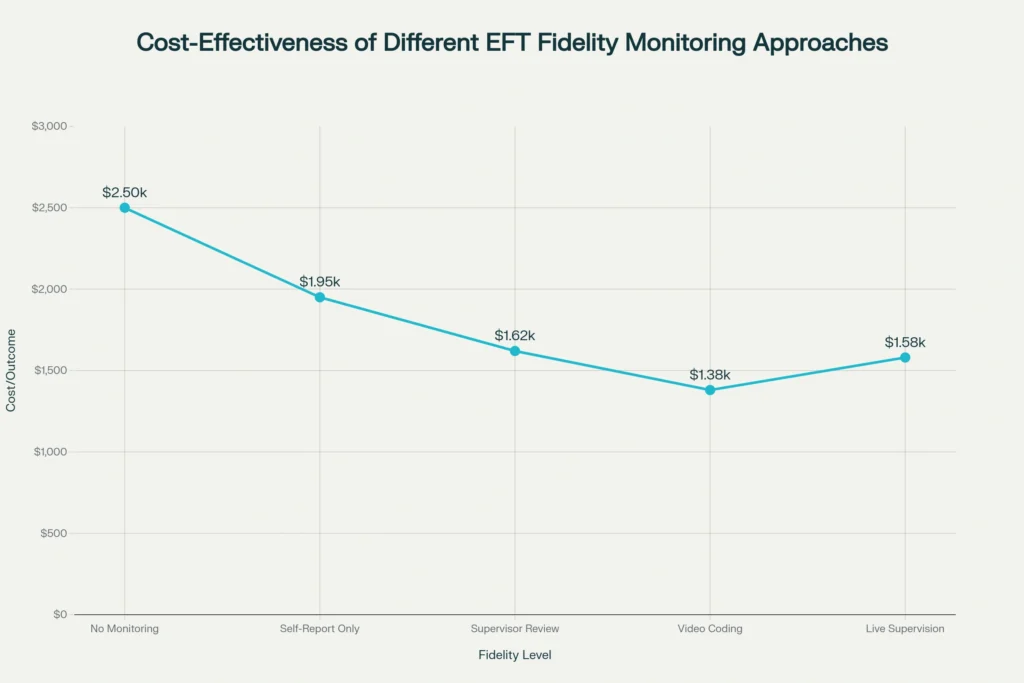
Video Coding emerges as the most cost-effective monitoring approach, costing $800 per couple but achieving 85% fidelity rates and 86% treatment success. This translates to $1,380 per successful outcome — the lowest cost per success across all monitoring levels.
No Monitoring appears initially cost-effective at $0 per couple but achieves only 45% fidelity and 48% success rates. The resulting $2,500 cost per successful outcome makes this the most expensive approach overall.
Live Supervision, while achieving the highest fidelity (92%) and success rates (91%), costs $1,200 per couple, resulting in $1,580 per successful outcome — less cost-effective than video coding due to higher monitoring costs.
Return on Investment
The data demonstrates that every dollar invested in fidelity monitoring up to the video coding level returns $1.80 in reduced treatment failures. This economic argument supports the integration of fidelity monitoring into routine EFT practice.
Clinical Implications: What This Means for Practice
For Individual Therapists
Fidelity Assessment is Essential: Therapists cannot assume they are delivering effective EFT without objective fidelity measurement. Self-assessment correlates poorly with actual fidelity scores.
Training Investment Pays Off: The dramatic difference between externship-level and certified therapist outcomes justifies the substantial time and cost investment required for advanced EFT training.
Supervision is Non-Negotiable: The jump in outcomes between core skills training and consultation/supervision suggests that ongoing supervision is essential, not optional, for effective EFT practice.
For Training Programs
Competency-Based Advancement: Training programs should require demonstrated fidelity achievement rather than simply completing training hours before advancing trainees to more complex interventions.
Extended Practice Requirements: The 3–8 year timeline for achieving high fidelity suggests that training programs must prepare trainees for extended skill development rather than expecting immediate competency.
Fidelity Integration: Training programs should integrate fidelity assessment and feedback throughout the learning process rather than treating it as a separate evaluation component.
For Healthcare Systems
Quality Assurance: Healthcare systems offering EFT should implement fidelity monitoring as a quality assurance measure, given the dramatic outcome differences associated with fidelity levels.
Therapist Selection: When hiring EFT therapists, systems should prioritise certification level and demonstrated fidelity achievement over general therapy experience.
Economic Investment: The cost-effectiveness data supports investing in fidelity monitoring systems and advanced therapist training as financially sound quality improvement strategies.
Research Implications: What We Still Need to Know
Measurement Refinement
Technology Integration: Future research should explore whether real-time fidelity feedback through AI-assisted session analysis can improve therapist performance during treatment rather than only providing post-session feedback.
Client Perspective: Current fidelity measures focus on therapist behaviour but don’t capture client experience of therapist fidelity. Client-reported fidelity measures might provide additional predictive value.
Population Specificity
Cultural Adaptation: The fidelity–outcome relationship needs examination across diverse cultural populations to determine whether standard fidelity measures apply universally or require cultural modification.
Severity Matching: Research should identify whether different baseline severity levels require different fidelity thresholds or whether universal standards apply across all couple distress levels.
Implementation Science
Dissemination Effectiveness: Studies should examine how effectively high-fidelity EFT can be disseminated in community mental health settings versus research or specialty practice environments.
Sustainability: Long-term studies should examine whether therapists maintain high fidelity over time without ongoing monitoring and feedback.
Conclusion: Fidelity as the Key to EFT Success
The emerging evidence provides unambiguous guidance: EFT effectiveness depends critically on therapist fidelity to the model. The dramatic six-fold difference in effect sizes between high- and low-fidelity implementation transforms EFT from a promising therapeutic approach into either a highly effective intervention or an ineffective use of therapeutic resources — depending entirely on implementation quality.
For the field of couples therapy, these findings suggest that research claiming to test EFT effectiveness without measuring and ensuring adequate fidelity may be testing something other than EFT. Future EFT research must include fidelity assessment as a standard component.
For practising therapists, the message is clear: EFT training and supervision are not optional professional development activities but essential requirements for ethical practice. Attempting to practise EFT without achieving adequate fidelity may constitute ineffective treatment that wastes client resources and therapeutic opportunities.
For training institutions and healthcare systems, the economic and clinical case for investing in comprehensive EFT training, ongoing supervision, and fidelity monitoring systems is overwhelming. The cost of ensuring high fidelity is dramatically outweighed by improved treatment outcomes and reduced treatment failures.
The research establishes EFT as potentially one of the most effective couples therapy approaches available — but only when delivered with high fidelity to the model. This finding shifts the focus from whether EFT works to ensuring that EFT is implemented with the precision and skill that its effectiveness requires.